- Understanding your motherboard components and their functions is simple... Join us as we explain the different parts of a motherboard with pictures.
- At the first glance, the components of a motherboard can appear complicated... even daunting to some. How are we supposed to figure out that jumble of connectors, ports, slots, sockets and heat sinks?
- The good news: To find your way around a motherboard, all you'll need to know are the major motherboard parts and their functions.
- And what better way is there... than to do it with labelled photos? Let's take a closer look at the different motherboard components below:
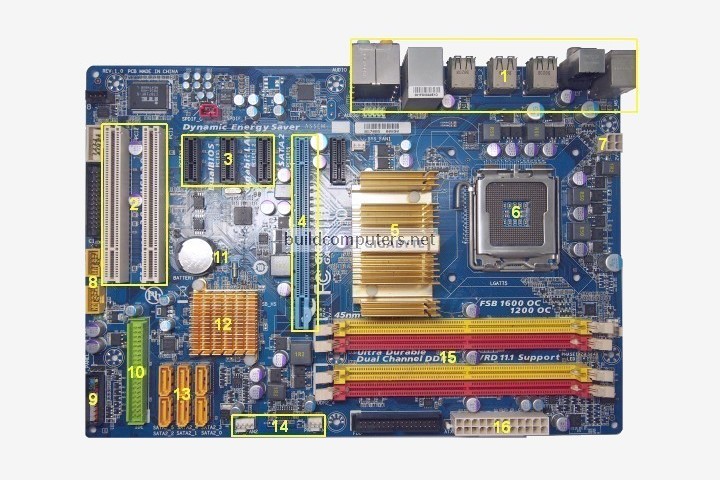
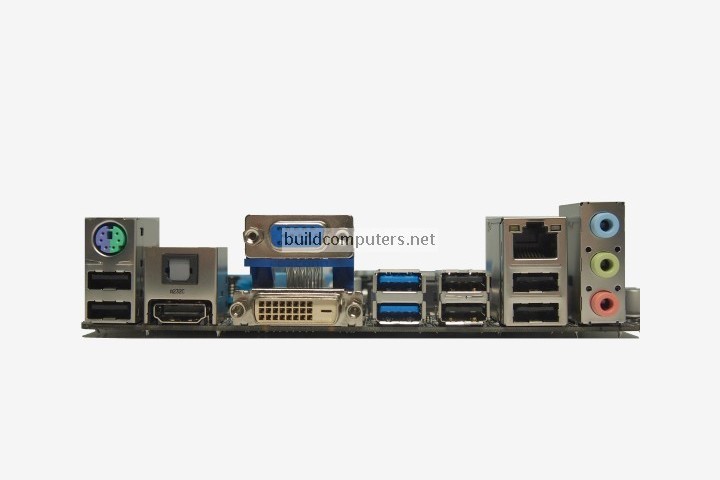
1. Back Panel Connectors & Ports :-
Connectors and ports for connecting the computer to external devices such as display ports, audio ports, USB ports, Ethernet ports, PS/2 ports etc. See image below for a close-up view.

2. PCI Slots :-
PCI: Peripheral Component Interconnect
Slot for older expansion cards such as sound cards, network cards, connector cards.
3. PCI Express x1 Slots :-
Slot for modern expansion cards such as sound cards, network cards (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Bluetooth), connector cards (USB, FireWire, eSATA) and certain low-end graphics cards.
4. PCI Express x16 Slot :-
Slot for discrete graphic cards and high bandwidth devices such as top-end solid state drives.

5. Northbridge :-
Also known as Memory Controller Hub (MCH).
Chipset that allows the CPU to communicate with the RAM and graphics card.
Beginning from the Sandy Bridge generation of Intel CPUs, motherboards no longer have this component as it has been integrated within the CPU itself.
6. CPU Socket :-
A CPU (Centrel Processing Unit) is the brains of your computer.

7. ATX 12V Power Connector :-
Connects to the 4-pin power cable of a power supply unit which supplies power to the CPU.

8. Front Panel USB 2.0 Connectors :-
Connects to USB 2.0 ports at the front or top of a computer case.

9. Front Panel Connectors :-
Connects to the power switch, reset switch, power LED, hard drive LED and front audio ports of a computer case.
10. IDE Connector :-
Connects to older hard drive disks and optical drives for data transfer.

11. CMOS Battery :-
Supplies power to store BIOS settings and keep the real-time clock running.
Also known As Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor.

12. Southbridge :-
Also known as the Input/Output Controller Hub (ICH).
Chipset that allows the CPU to communicate with PCI slots, PCI-Express x 1 slots (expansion cards), SATA connectors (hard drives, optical drives), USB ports (USB devices), Ethernet ports and on-board audio.

13. SATA Connectors :-
Connects to modern hard disk drives, solid state drives and optical drives for data transfer.

14. Fan Headers :-
Supplies power to the CPU heat sink fan and computer case fans.

15. RAM Slots :-
Rendom Access Memory. RAM memory is easy but there are important details to know and mistakes to avoid.

16. ATX Power Connector :-
Connects to the 24-pin ATX power cable of a power supply unit which supplies power to the motherboard.
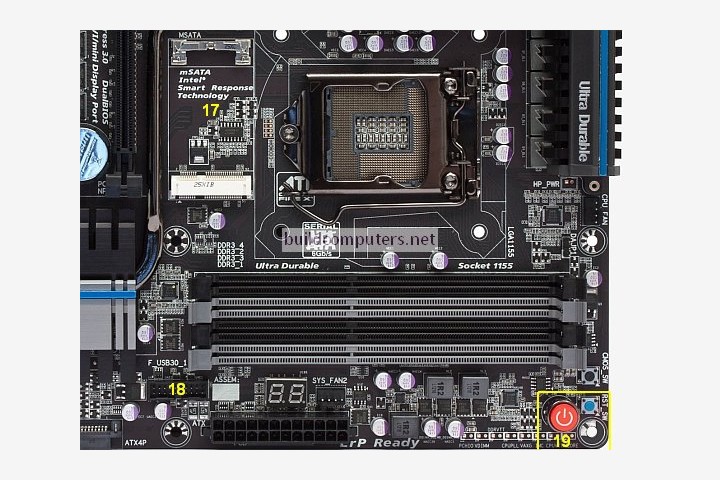


17. mSATA Connector :-
Connects to a mSATA solid state drive. In most cases, this SSD is used as cache to speed up hard disk drives, but it's possible to re-purpose it as a regular hard drive.

18. Front Panel USB 3.0 Connector :-
Connects to USB 3.0 ports at the front or top of the computer case.
19. Power & Reset Button :-
Onboard button to turn on, turn off and reboot the computer.

NOTE :- This motherboard component is more common among high end boards
No comments:
Post a Comment